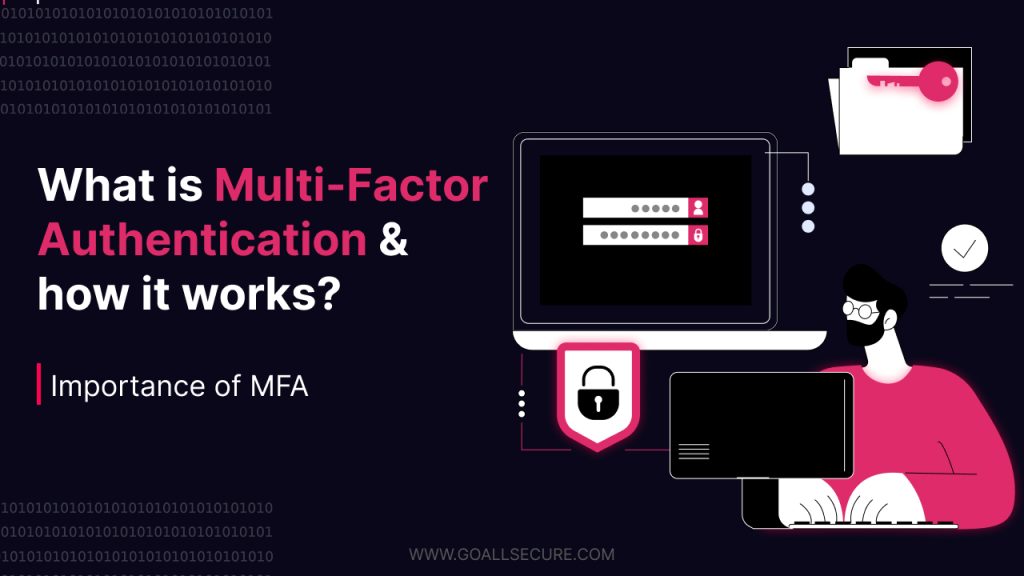
According to a report, credential compromise and phishing are two of the most popular cyberattack methods. When combined, they represent 41% of all data breaches. Passwords are frequently stolen by both vectors, which indicates a need for a robust security mechanism. Multi-factor authentication is a god sent solution. In today’s world, where sensitive data is stored online by individuals and corporations, digital security is paramount. Everyone uses online accounts to interact with internet-stored programs, services, and data. A breach or exploitation of this online data could cause significant repercussions, including loss of privacy, financial theft, and commercial interruption. Luckily, MFA can help you avoid such circumstances. In this blog, we will talk about multi-factor authentication, its types, and its importance in cyber security.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication?
As we know, using just one type of authentication is no longer safe as cyber threats are becoming more complex. Compromising passwords using brute force, cracking, or phishing techniques is easier. Multi-factor authentication greatly increases the difficulty of unauthorised access by adding more security layers. MFA makes sure that even in the unusual event that one factor is compromised, unauthorised people are unlikely to be able to access the system by needing multiple kinds of authentication. MFA is a security mechanism that involves numerous authentication methods from different categories of credentials to confirm a user’s identity during a login or other transaction. Users must submit more information than passwords during the multi-step account login process. This information could be biometric verification, a code delivered to their email, a secret question to answer, or a security key. An additional authentication method prevents unwanted account access if a system password is hacked.
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
MFA functions by confirming that a user is authorised to access an account by needing one or more authentication methods and a standard password. When a user registers for an account, several kinds of identification are requested to facilitate multi-factor authentication. In order to authenticate the user for the subsequent login, the system saves this ID and user data. Because it is harder for a cybercriminal to compromise two authentication factors at once than it is to breach one, this provides an additional layer of security. The multi-step login process confirms additional ID details in addition to the password whenever someone tries to log in.
Furthermore, MFA has the ability to adapt, offering security flexibility. More sensitive information may require several authentication mechanisms, while access to less sensitive data may require a few. This flexibility makes security better and makes using the system more enjoyable because it removes needless obstacles from lower-risk activities.
Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication in Cyber Security
Multi-factor authorisation is crucial to maintaining one’s safety online, be it at an individual or organisation level. Think of it similar to multiple layers of physical security, like a guard station, an ID scanner, locks on the doors, and a fence with a gate that one might use to protect their property. An organisation can use MFA to provide multiple layers of virtual security to ensure that anyone accessing the system, onsite or remotely, is authorised and authenticated. Why is Multi-factor authentication necessary when you have passwords? Well, passwords do safeguard digital assets, but they are insufficient. Skilled cybercriminals frequently search for passwords. If someone finds out your password, they could access several accounts you may have used it for. In the case that the password is compromised, MFA provides a second layer of protection to keep malicious actors from accessing these accounts.
Companies employ multi-factor authentication as one of the most important cyber security trends to confirm user identities and give authorised users easy access. Doing so ensures that there is an added layer of security in an adverse situation. MFA aims to strengthen security and provide a layered defence so that a targeted cyber attacker would have at least one more barrier to overcome before successfully accessing the actual targeted device, even if one factor—the username and password—is compromised. So, with MFA in place, you are better shielded against more sophisticated cyber attacks. There are various other benefits to using multi-factor authentication:
- In-depth defence
- Increased productivity and flexibility
- Protection against fraud
- Enhanced customer trust
- Improved identity protection
- Safer environment for remote work
- Enhanced overall data protection
Understanding Various Factors Of Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA uses different types of authentication factors for credentials used for identity verification. Each and every additional feature added to an MFA request aims to strengthen the confidence that the party requesting access to a system or engaging in communication is who or what it says it is. These authentication factors are different from your usual usernames and passwords. Proper multi-factor authentication systems use at least more than one distinct type of authentication element. Because hackers will need to employ unique techniques across numerous channels to crack each factor, employing different kinds of factors is seen to be more secure than using multiple factors of the same kind. These elements of authentication could be something they possess, something they know, something they are, etc. Some popular authentication techniques used by MFA to confirm a user’s identity are:
- Knowledge
- Possession
- Inherence
- Location
- Time
The most popular authentication techniques are knowledge, possession, and inherence. Let’s discuss them one by one.
Knowledge: Knowledge factors are information or details like passwords, PINs, and security question answers that, in theory, only the user would know. The first component in most MFA setups is knowledge factors, which are typically passwords. This is the element with which users are most acquainted.
Possession: This component uses something the user owns to confirm their identity. A person’s possessions that they can use to establish their identification are known as possession factors. Both tangible hardware tokens and digital software tokens are considered possession elements. Physical elements are external to the network and are typically hard to fake.
Inherence: This component uses a distinctive personal characteristic, such as voice recognition or biometric identification, to confirm an individual’s identity. Face scanners and fingerprint readers are standard on laptops and smartphones, and many websites and applications can use this biometric information as an authentication element.
Examples of Multi-Factor Authentication
A password serves as the most apparent MFA factor. While some multi-factor authentication systems are completely passwordless, many still require passwords in addition to other factors. These are typical elements that are added to, or used in place of, conventional password authentication. Specific authentication techniques are more secure than others because they use different approaches to verify identities. The three categories of factors discussed above contain various verification techniques. An organisation can implement multifactor authentication in a variety of ways. Here are some examples of the most typical techniques a user will encounter in their digital life.
1. Email tokens
Email codes are frequently used as part of MFA. When you try to log in, a unique code is emailed to your registered email address. After that, in order to confirm your identity, you must enter this code on the login page. Email codes have the benefit of being user-friendly and straightforward for end users. However, the degree of security of the email account will determine how secure this method will be. Thus, it’s imperative to guarantee that users have implemented robust email security protocols.
2. SMS tokens
This MFA procedure uses SMS, or short messaging services, which are shared during the login stages. When registering using this technique, the user must provide their phone number. After setting up and verifying their phone number, an additional identification check takes place, which involves having an SMS delivered to their verified phone each time they visit the website. The user will be prompted to provide this SMS code after logging in with their credentials.
3. OTP(text or call)
Another popular MFA technique is using one-time passwords (OTPs) sent by phone or text message. When you attempt to log in, an OTP is delivered to your registered mobile number. The next step is to verify your identity on the login screen by entering this OTP. This authentication technique is very simple to use as it is fuss free.
4. Biometric Authentication
One MFA option that is expanding quickly is biometric verification. It entails utilising distinctive behavioural or physical traits to confirm an individual’s identity. These traits may include retinal scanning, voice recognition, facial recognition, and fingerprints. Because biometric information is specific to each person, it is challenging to falsify or steal, which is one benefit of biometric verification.
5. Hardware Security Key
A tangible token is a hardware security key. Once it’s linked to your accounts, you should store it somewhere safe so that you won’t misplace it. Typically, you will tap the key on your smartphone or insert it into a USB port to access your account. Once the key is detected, your device will verify your identity. It is difficult for a cybercriminal to steal this authentication mechanism via the internet, making it one of the most secure. This technique could only be jeopardised if the physical key was stolen or misplaced.
6. Authenticator Apps
An increasingly common but somewhat recent MFA technique is the use of authenticator applications. These applications produce one-time passwords (OTPs), which you enter on the login page to authenticate yourself. This approach has the advantage of not depending on your email address or phone number, both of which are vulnerable to hacking.
7. Security Questions
Although security questions are a far more straightforward type of MFA, they can still be helpful if utilised appropriately. Specific enquiries, such as the name of a pet or the user’s first job, should only have an answer that the user knows. But it’s crucial to remember that security questions shouldn’t ever be the only way to authenticate. The most excellent application for them is in combination with other techniques, such as fingerprint scans or passwords. This is because social engineering techniques can frequently be used to guess or obtain the answers to security questions.
Conclusion
Making sure your accounts are safe from malevolent threat actors is crucial as we depend more and more on apps and accounts for daily business operations. Multi-factor authentication is a simple and practical solution for safeguarding our digital lives at home and at work. Multi-factor authentication techniques combine your password and username, making it more difficult for an attacker to gain access, even if they know your password. To guarantee the highest level of account security, GoAllSecure strongly advises all organisations to use multi-factor authentication wherever it is practical. Your organisation’s Identity and Access Management (IAM) will be strong, and a solid MFA configuration will protect your resources. You can find the best solution for your company with us rather than waiting to be hacked. Our team will enable you to stop hackers in their tracks and make your digital realm safer. Don’t hesitate to contact us at +91 85 2723 7851 or +44 20 3287 4253 if you have questions about multi-factor authentication. Take caution, and be safe.















 TRAVEL & HOSPITALITY
TRAVEL & HOSPITALITY HEALTHCARE
HEALTHCARE RETAILS & ECOMMERCE
RETAILS & ECOMMERCE BANKING & FINANCIAL
BANKING & FINANCIAL AutoMobile
AutoMobile MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING FOOD
FOOD EDUCATION
EDUCATION